Marijuana, also known as cannabis, weed, pot, or dope, refers to the dried flowers, leaves, stems, and seeds of the cannabis plant. This plant contains over 100 compounds or cannabinoids, including tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), which is impairing, and cannabidiol (CBD), which is not impairing. In the United States, marijuana is classified as a Schedule I substance under the Controlled Substances Act, indicating it has a high potential for abuse and no accepted medical use under federal law.
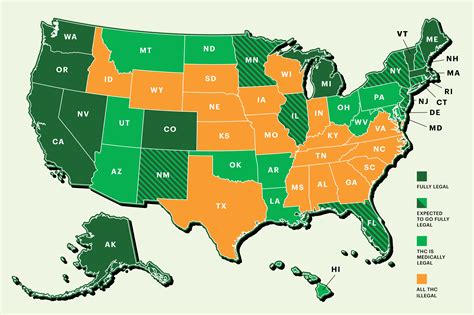
Despite federal restrictions, cannabis use was legal in the 1800s and widely utilized therapeutically. However, after the advent of synthetic painkillers and heightened media attention on cannabis-related violence, Congress banned recreational use in 1937. Currently, state and federal laws often conflict when it comes to cannabis possession and use. While some states have legalized cannabis for recreational and medical purposes, federal prohibition laws still apply. As of March 1, 2023, 21 states, along with DC, Guam, and the Northern Mariana Islands, have enacted laws permitting recreational marijuana use.
In California, cannabis is legal, and you can purchase it if you are 18 or older with a physician’s recommendation for medicinal use, or 21 or older for adult use. Local jurisdictions may impose stricter laws than the state. For the latest rules in your area, it is recommended to check your city or county website. President Biden has indicated that although federal and state regulations may evolve, important restrictions on trafficking, marketing, and sales to minors should remain in effect.
Marijuana can be consumed in various ways, including smoking in joints or blunts, using bongs, or being infused into edibles like cookies, cakes, or drinks.
For more detailed information, please refer to the following sources:
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
DEA.gov
Cannabis legalization in the US
Cannabis & the law guide – Texas